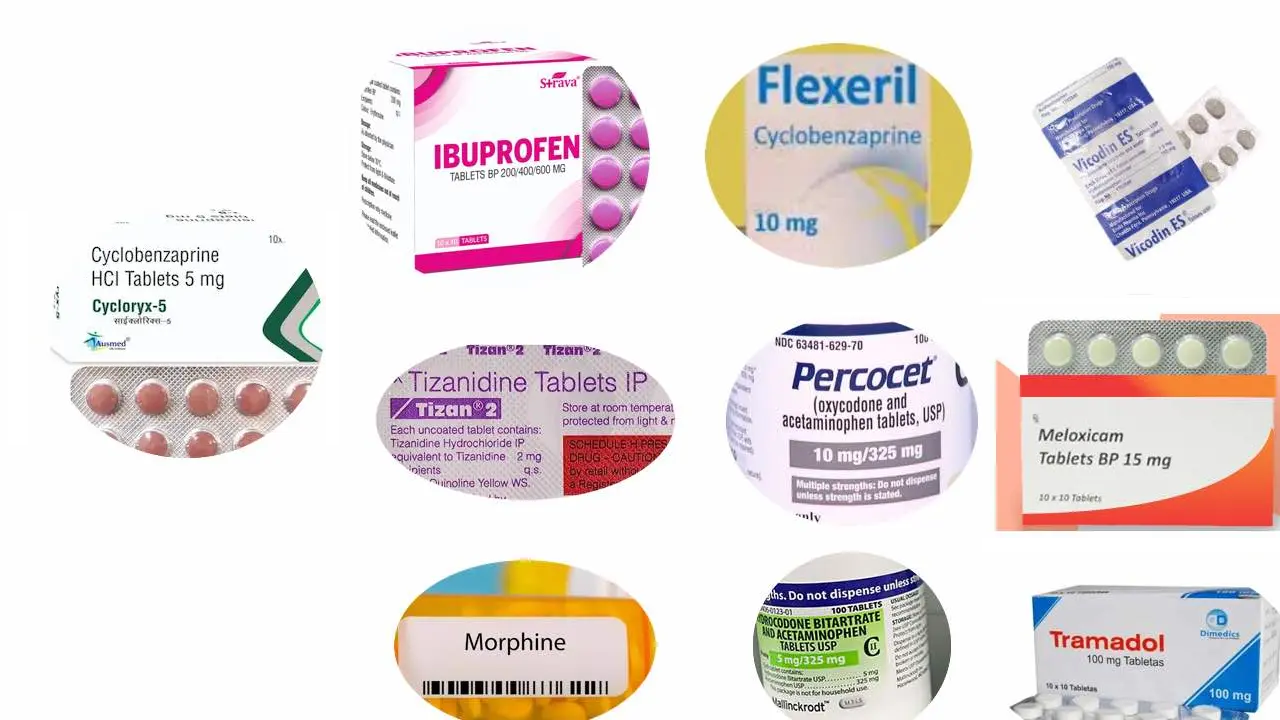
Cyclobenzaprine is a muscle relaxant medication primarily used to treat skeletal muscle spasms and relieve pain caused by musculoskeletal conditions. It works by blocking nerve impulses that cause muscle spasms and cramping. Cyclobenzaprine is often prescribed for conditions such as fibromyalgia, back pain, and neck pain.
Cyclobenzaprine Dosages
The typical dosage of cyclobenzaprine is 5 mg to 10 mg taken three times daily. For more severe muscle spasms, a higher dose of up to 30 mg per day may be prescribed, divided into multiple doses. It’s crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and not exceed the recommended limit.
Cyclobenzaprine Best Alternative
Tramadol
Tramadol is a centrally acting opioid analgesic used to treat moderate to severe pain. While it does not have direct muscle relaxant properties like cyclobenzaprine, it can effectively manage pain associated with muscle spasms and cramping. Order Tramadol 100mg and Get Discount on instant Order. However, tramadol carries a higher risk of dependence and addiction compared to cyclobenzaprine.
Vicodin
Vicodin is a combination of hydrocodone (an opioid) and acetaminophen. It is a potent pain reliever commonly prescribed for moderate to severe pain. Like tramadol, Vicodin does not have muscle relaxant effects but can provide relief from pain caused by muscle spasms. However, it also carries a higher risk of addiction and side effects compared to cyclobenzaprine.
Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that can help reduce inflammation and pain associated with muscle spasms. While it does not have direct muscle relaxant properties, ibuprofen can be an effective alternative for managing muscle spasm-related discomfort, especially when inflammation is a contributing factor.
Tizanidine
Tizanidine is another muscle relaxant medication that works by blocking nerve impulses responsible for muscle spasms and cramping. It has a similar mechanism of action to cyclobenzaprine and can be an effective alternative for treating muscle spasms and related pain.
Morphine
Morphine is a strong opioid analgesic used for severe pain management. While it does not have muscle relaxant effects, morphine can effectively relieve pain associated with muscle spasms. However, it is a highly potent medication with a higher risk of addiction and side effects compared to cyclobenzaprine, and is typically reserved for severe, chronic pain cases when other options are not effective.
Flexeril
Flexeril is a brand name for cyclobenzaprine. It is essentially the same medication as cyclobenzaprine and is used for treating muscle spasms and related pain.
Norco
Norco is a combination of hydrocodone (an opioid) and acetaminophen, similar to Vicodin. It is a potent pain reliever commonly prescribed for moderate to severe pain but does not have direct muscle relaxant properties.
Percocet
Percocet is a combination of oxycodone (an opioid) and acetaminophen. Like Norco and Vicodin, it is a strong pain medication used for moderate to severe pain but does not have muscle relaxant effects.
Statistics:
- According to a study published in the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, cyclobenzaprine was found to be more effective than placebo in reducing muscle spasm and pain, with a similar side effect profile to other muscle relaxants. (Source: https://www.cochranelibrary.com/cdsr/doi/10.1002/14651858.CD009786.pub2/full)
- A study in the Journal of Pain Research reported that cyclobenzaprine provided significant improvement in fibromyalgia symptoms, including muscle pain and tenderness, compared to placebo. (Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5469612/)
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that approximately 20.4% of U.S. adults had chronic pain in 2019, with back pain and neck pain being among the most common types, often associated with muscle spasms. (Source: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/databriefs/db390.htm)